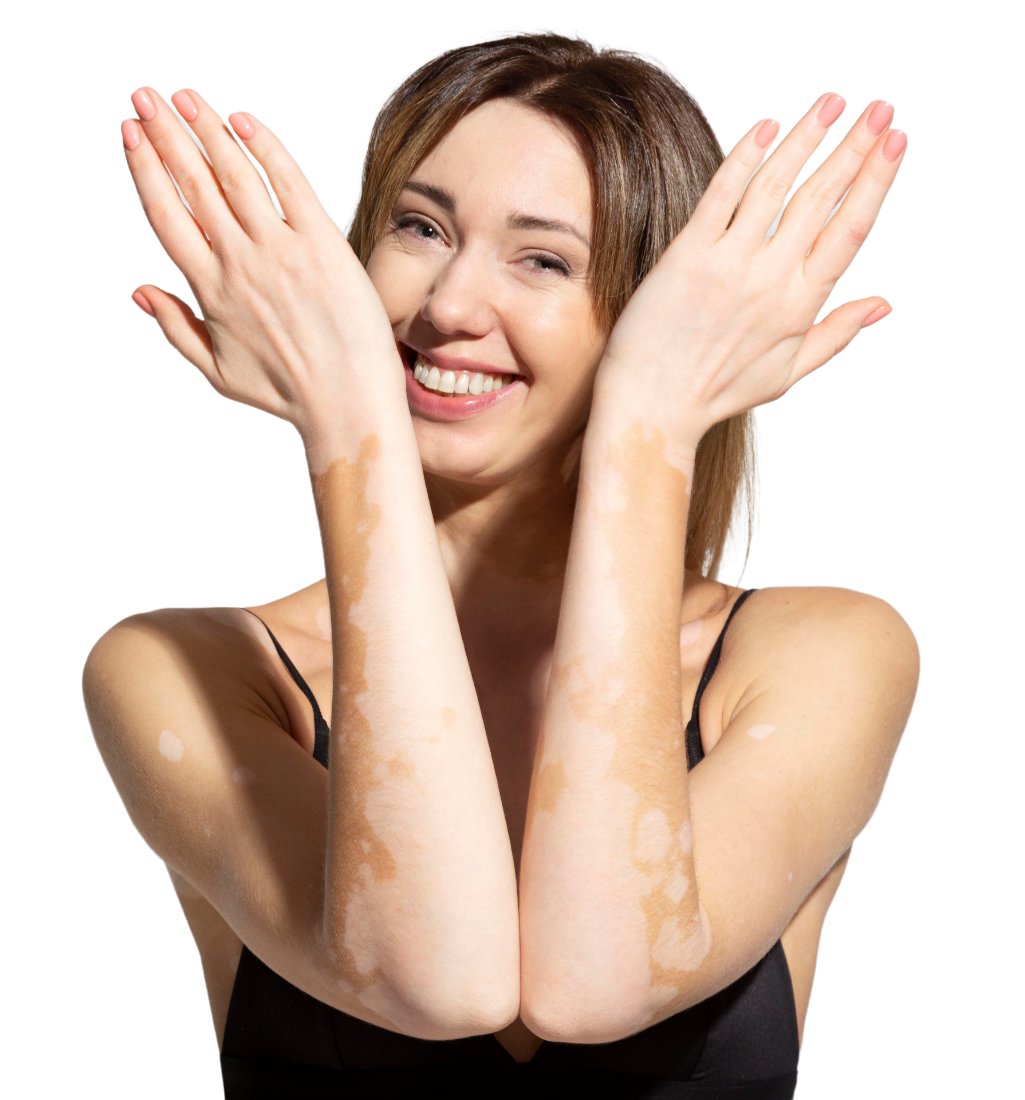
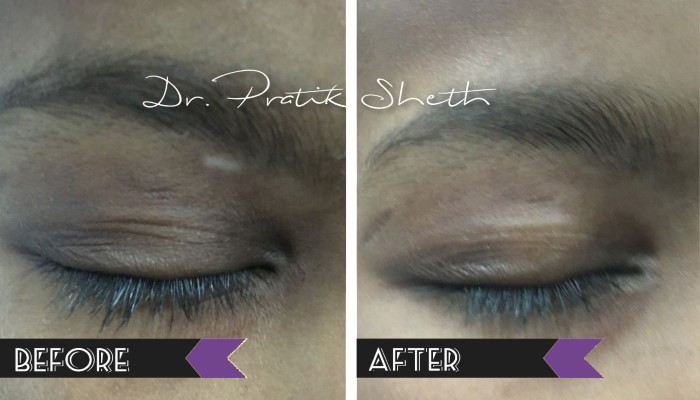
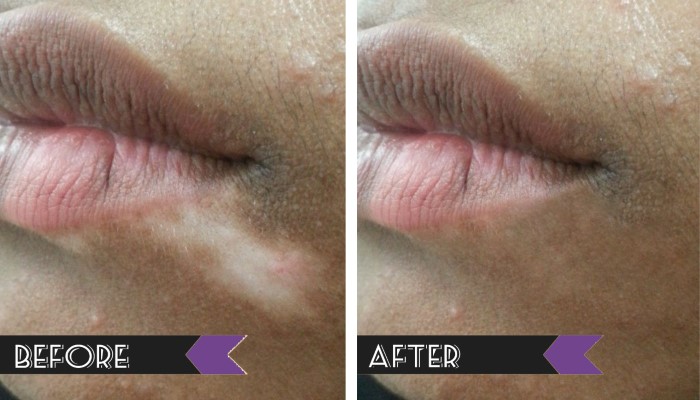
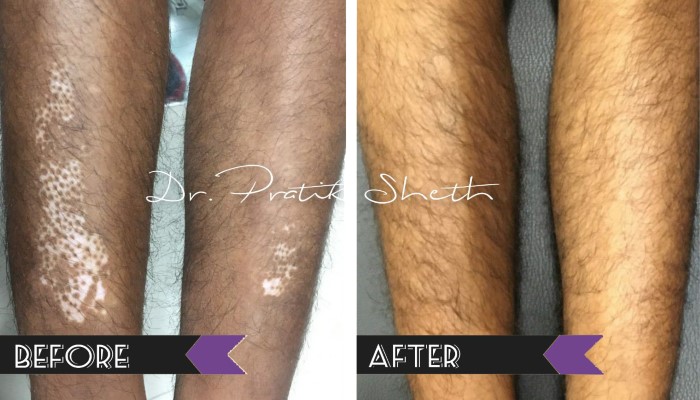
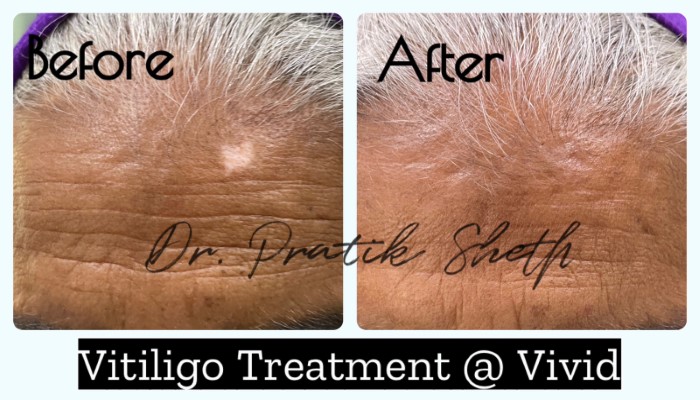
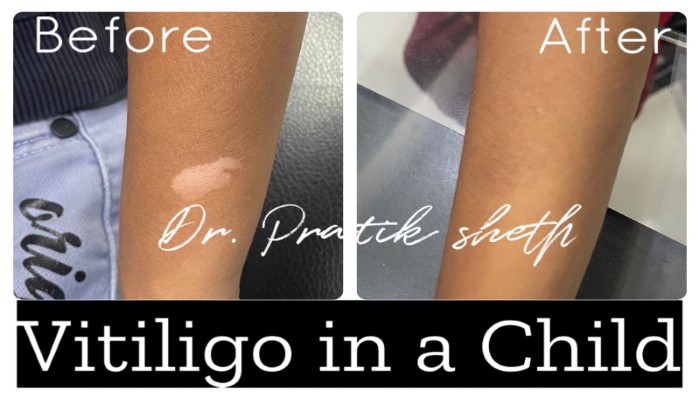
Vitiligo Treatment
Leuco= White, Derma = Skin, i.e. Leucoderma means a WHITE SKIN.
There are many conditions in which skin can become white (Depigmentation) and vitiligo is one of the cause.
Other causes of leucoderma are chemical leucoderma, genetic leucoderma (Piebaldism) Leucoderma in other diseases like SLE, Systemic sclerosis, etc.
 Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin disease in which the immune cells of the patient's body destroy his/her our own melanocytes (cells which forms pigmentation in skin), resulting in white patches due to the loss of pigment.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin disease in which the immune cells of the patient's body destroy his/her our own melanocytes (cells which forms pigmentation in skin), resulting in white patches due to the loss of pigment.
People use the term Safed Daag / Kodh / Kusta Rog etc. in Gujarati or Hindi for white patches, though every white patch is not vitiligo.
Anyone can get vitiligo, and it can develop at any age.
Vitiligo seems to be more common in people who have a family history of the disorder or who have certain autoimmune diseases, including:
- Addison’s disease.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Psoriasis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Thyroid disease.
- Type 1 diabetes.
White patches can appear anywhere on your body and can affect:
- Skin, which develops milky-white patches, usually on the hands, feet, arms, and face. However, the patches can appear anywhere.
- Hair, which can turn white in areas where the skin is losing pigment. This can happen on the scalp, eyebrow, eyelash, and beard.
- Mucous membranes, such as the inside of your mouth or nose.
People with vitiligo can also develop:
- Low self-esteem or a poor self-image from concerns about appearance, which can affect quality of life.
- Uveitis, a general term that describes inflammation or swelling in the eye.
- Inflammation in the ear.
- Immune system disorder (Most common cause)
- Heriditary
- Stress
- Exposure to some chemicals
- Trauma / Injury
- Sun burn
Vitiligo can be of following types:
- Focal vitiligo – Single small lesion
- Vitiligo vulgaris – Generalised vitiligo – Multiple whitish patches on all over body
- Lip-Tip Vitiligo – More confined on lips and finger tips
- Segmental vitiligo – Vitiligo on particular segment of body
Vitiligo can be easily diagnosed clinically by dermatologist.
A dermotologist can confirm it by examining white patches by Wood's lamp.
Other tests can include:
- Blood tests are done to plan therapy to control the spread of vitiligo and to rule out any other associated conditions like hypothyroidism or other autoimmune conditions. Blood tests to check for other autoimmune diseases.
- An eye exam to check for uveitis, an inflammation of part of the eye that sometimes occurs with vitiligo.
- A skin biopsy, which means taking a small sample of your skin to be examined under a microscope. Doctors can examine the tissue for the missing melanocytes seen in the depigmented skin of a person with vitiligo.
"Vitiligo itself is not harmful."
Due to its autoimmune nature, white patches can increase in size or spread to other parts of body
But it mostly affects the person psychologically due to visible nature of white patches and social stigma attached to it. Women are generally more psychologically affected than men.
Vitiligo is poorly understood in many communities. It is often confused with leprosy or sexual infections and even seen as a sin or a sort of punishment sent by God- which is NOT TRUE.
"It is not only for what we do, that we are responsible, but also for what we do not do."
If you are facing any of the situations mentioned below, then there are high chances that white patches on your skin are having tremendous psycho-social impact in your daily life.
-
Anxiety, Stress, Depression

-
Hiding face

-
Avoid going to school or office

-
Fear of losing marriage proposals

-
Low self confidence

-
Constantly think what others think about you

-
Problems in marrital relationship

-
Spending most of time doing makeup to hide acne

-
Being self concious

-
Face situations where people stare at your acne

It's not necessary that all of above will be present. These effects gradually develop over time.
Feeling of even a single condition as mentioned above is significant.
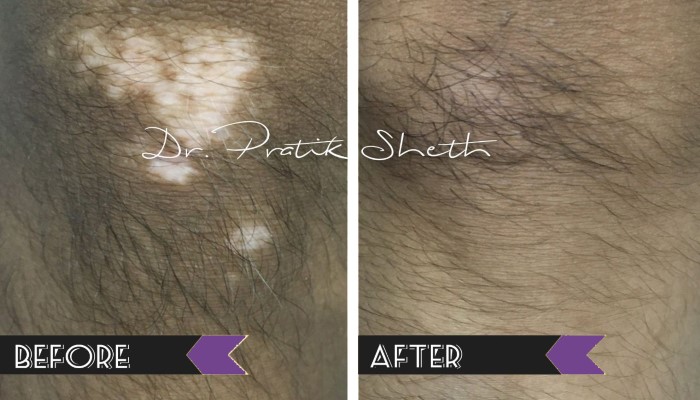
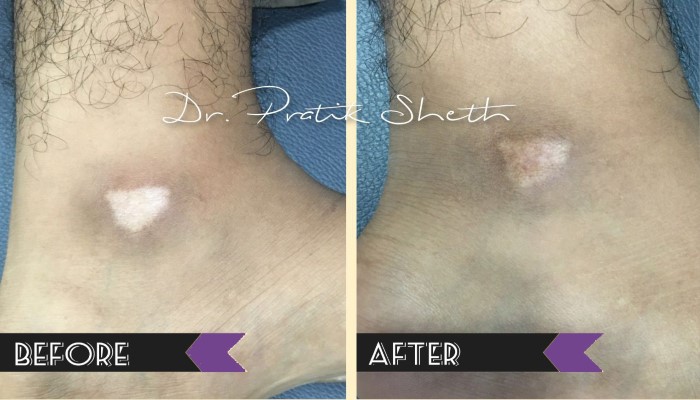
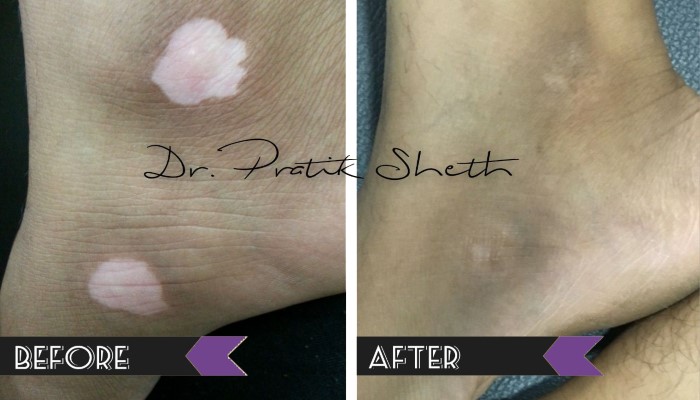
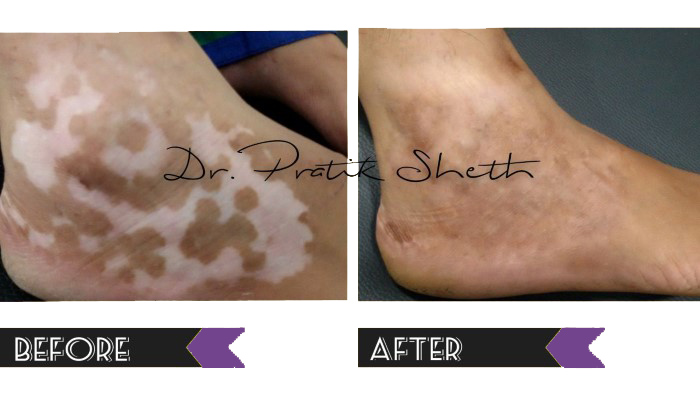
There are broadly three options for leucoderma / vitiligo treatment in Rajkot.
A. Medical Treatment: For active or inactive form of vitiligo and as a part of treatment after surgery.
1️⃣. Oral Medicines and topical creams / oint / gel
2️⃣. Photo-chemo-therapy (PUVA or PUVASOL)
3️⃣. Photo-therapy (NB-UVB)
4️⃣. Excimer light therapy
Usually single treatment option is not effective alone, so a combination of above options is usually done to achieve good and fast response.
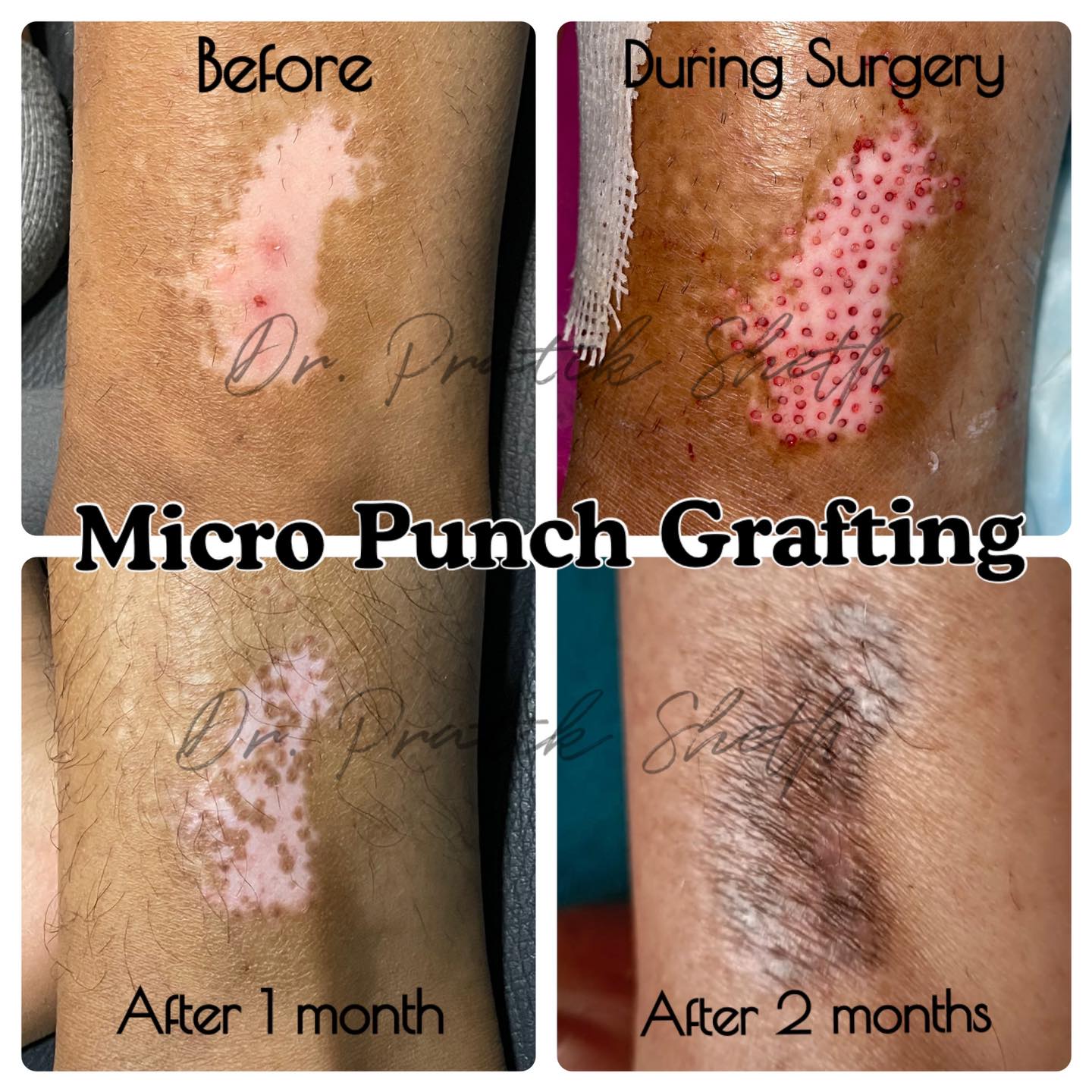
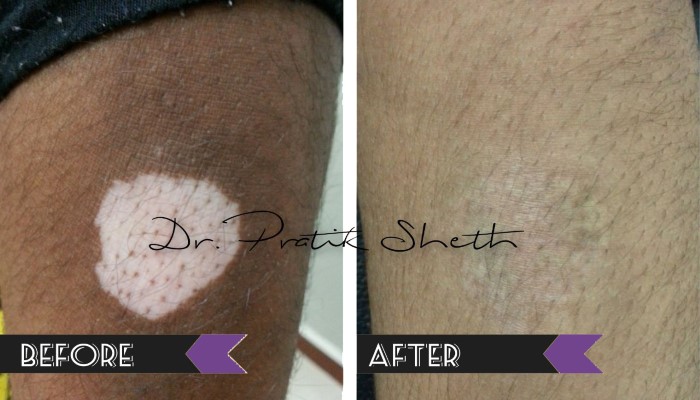
B. Vitiligo Surgery: Only for inactive or stable form of vitiligo, not responding to medical treatment.
3️⃣. Micro punch grafting
Surgery is typically not recommended when vitiligo is spreading or for people who scar easily or develop keloids.
C. Other Treatment Options: If not opting / not responding to above options, then
1️⃣. Psychological treatment / support
2️⃣. Skin camouflage
3️⃣. Complete skin whitening therapy (for extensive vitiligo)
Most treatments for vitiligo focus on stopping the immune system from destroying the melanocytes and improving the skin’s appearance.
In most cases, the goals of your treatment are to:
- Slow or stop the disease from progressing.
- Encourage the regrowth of melanocytes.
- Restore color to the white patches of skin, which can help the skin color look more even.
It’s important to remember that treatments may take time, and not everyone responds. In addition, the results from treatments can vary from one part of the body to another, and new patches may appear in the meantime. Sometimes, doctors will recommend more than one treatment to get the best results.



- Protect your skin from sunlight, Try to avoid sunlight between 11am to 3pm, wear full clothing, use broad spectrum sunscreen.
- Apply good amount of moisturiser.
- Avoid trauma to the skin since traumatic area can turn white because of vitiligo activity.